Machine learning models, like humans, also make mistakes. With mistakes, machine models learn and improve, hence they are growing rapidly throughout the world. And they do all that with a hyperparameter known as the learning rate. One might ask What Is the Learning Rate In Machine Learning?. It’s a measure of how efficiently our model learns from its mistakes and updates its knowledge to fix errors. While training a model, the first priority is to reduce the errors and optimize the model effectively. The learning rate is used to do the job.
What Is the Learning Rate In Machine Learning?
The learning rate is an integral part of machine learning algorithm optimization. Simply put, it helps the model identify mistakes and make changes to improve it for future use. Let’s understand one thing first: machine learning operates on two parameters: hyperparameters and machine-learnable parameters. We are working with a hyperparameter: the Learning Rate. Scientists or engineers provide numeric values to the machine to keep it updated.
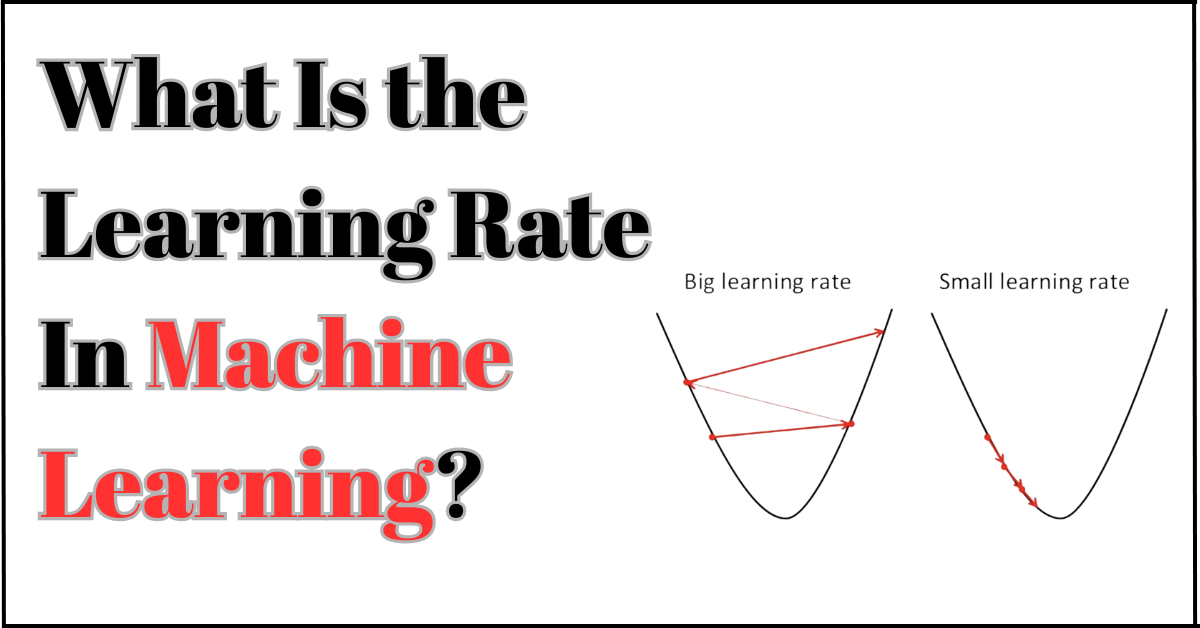
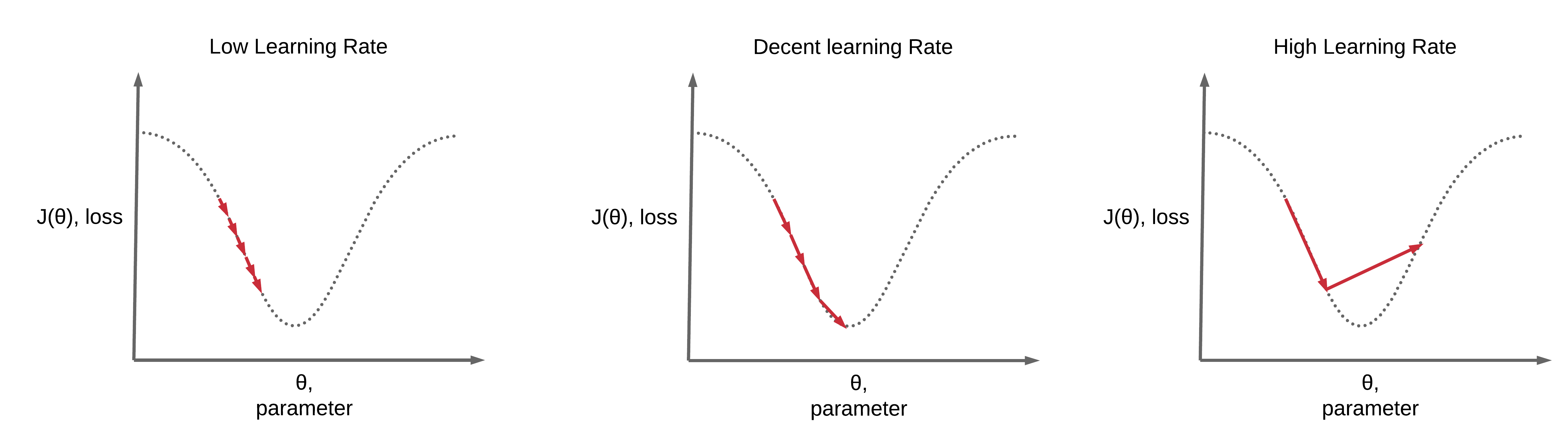
Machine learning models use gradient descent algorithms for maintenance. Now what is gradient descent? These are adjustment models that computers use to maintain a check-and-balance. The learning rate is a sub-branch, also called the step size. Basically, it checks whether the steps to fix the errors are followed correctly. If the step size is too small, the epoch training time is longer, and the learning rate is lower. If it’s too big, the epoch is shorter, the system might skip the actual point, and fail to perform its job.
Analogy And Understanding
Let’s bring it into a real-world context. Suppose a patient is prescribed a 100mg tablet for his disease. If given 500mg, it indicates a high learning rate and may produce a toxic effect, which is not desired. Similarly, if we give 5mg, then it’s a small learning rate, and the patient will take forever to recover.
Importance Of Learning Rate
Optimization and learning of AI models are heavily dependent upon learning rates. It helps machine learning models to optimize their training without overshooting or slow convergence. With high learning rates, the system would jump over the problem and make things more complex, rather than simplifying it.
If it’s set at very low values, the system would be stuck forever to reach its maximum effectiveness. Both parameters are against our requirement. Setting an optimal learning rate is a complex task that requires a trial-and-error approach to find the perfect balance. When key balance is reached, the model works perfectly, addresses the problem effectively, and corrects it at the right rates.
Commonly Used Learning Rates
The learning rate is a hyperparameter, meaning the programmers set the values that determine the speed of learning rate. It is usually between 0 and 1. Finding the best learning rate for a model is a challenging task. Multiple people ask is 0.001 a good learning rate?, it depends on the type of model being trained. The best strategy is to start at a higher value. Then decrease the learning rate as long as accuracy is increasing and loss is decreasing, until the best value is found. typically used rates are 0.1(1e-1),0.01(1e-2), 0.001(1e-3),0.0001(1e-4).
Slow learning Rate (0.0001)
A slow learning rate is a good choice when the data is noisy and the model is sensitive. When you don’t want slight updates to be missed. But it will take a longer time and require more epochs.
Large Learning Rate (0.1)
Large learning rates (0.1) are better if you want faster updates, and speed is the key. The risk of overconvergence increases with these high rates, which would speed up learning but keep learning minimal.
Medium Learning Rate (0.001)
There is no right or wrong rate; it all comes down to: the type of model being trained. Most people prefer medium rates, as they are safe for fast speeds and learning.
FAQ’s
Q1: What is the learning rate of a machine learning model?
The learning rate is a hyperparameter that determines how quickly the system updates itself in response to the loss function during optimization. A low learning rate means slower convergence. High learning rate could lead to overlooking the root cause and jumping to a conclusion.
Q2: Is 0.001 a good learning rate?
0.001 is often considered a good learning rate and used in SGDs to optimize the model. It is considered a decent balance between speed and deep learning training of the model. There is no perfect learning rate; it depends on the type and resources of the model that is being optimized.
Q3: What is a loss function?
A loss function is also called an error function. It measures the deviation or error between a machine learning model’s prediction and the actual target. If the model predicts accurately, the loss is small; if it makes a big mistake, the loss is large. To correct it, the model is updated using learning rates.
Q4: What is gradient descent
Gradient descent is the main head of all the updates. It is an optimization algorithm. It uses parameters such as the learning rate to reduce the loss function in the learning model, thereby improving the model’s performance.
Conclusion:
Machine learning models use different parameters, some are automated, some are decided by the scientist for the machine. One of these parameters is the learning rate. It helps the model better optimize and learn from its mistakes. It requires a right balance. If it’s too high, things deviate from the right decision. If it’s too low it takes ages to reach the optimal goal. Balance and model play a key role in deciding which learning rate is better. Most people use 0.001 learning rates for SGD, which hits the best of both worlds: the speed and deep learning.