Ever wondered how you know a machine learning model is “good”? Too often, people grab a single number and call it accurate. But accuracy is a simple mirror that sometimes lies. It tells you how frequently the model is right overall or not. Yet, it glosses over which mistakes matter.
This article peels back the curtain on what accuracy in machine learning really measures, shows the accuracy formula in machine learning, and explains when to reach for precision in machine learning, F1 score in machine learning, or other metrics, so you can judge models like a pro without being hoodwinked. Read on to sharpen your model-evaluation instincts.
What Is Machine Learning Accuracy? The Simple Scoreboard.
Machine learning accuracy is the fraction of predictions a model gets correct. Accuracy can be found out by:
Accuracy = the number of accurate predictions / the total number of predictions.
It answers a plain question: how often is the model right? This is straightforward and usually the first metric you will see when checking models. But simple does not mean sufficient accuracy. It can be deceptive when classes are imbalanced or when different errors have different costs.
Accuracy Formula in Machine Learning: The Math behind the Metric:
The accuracy formula in machine learning is compact:
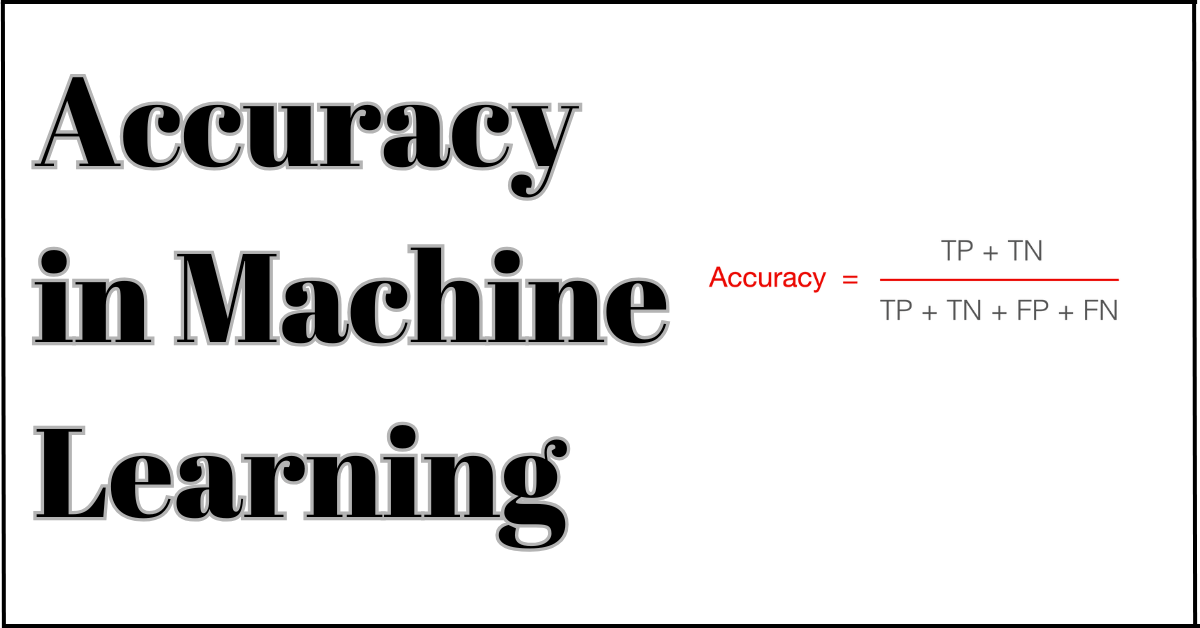
Accuracy = (TP + TN) / (TP + TN + FP + FN)
In the above formula, TP stands for true positives, TN stands for true negatives, FP stands for false positives, and FN stands for false negatives. This formula is typically used for interpretation and computation when working with libraries like scikit-learn. But remember, the formula treats every kind of error equally.
Machine Learning Accuracy Measures Class Imbalance and False Comforts:
If one class dominates your dataset (say, 95% “no disease”, 5% “disease”), a dumb model that always predicts “no disease” gets 95% accuracy, which looks great on paper but is worthless clinically. In such cases, machine learning accuracy gives you a false sense of security. That’s why practitioners use alternative metrics or balanced variants, such as balanced accuracy, which averages per-class recall. Do not fall for a high percentage if the model is ignoring the minority class you actually care about.
Precision in Machine Learning:
Precision in machine learning is literally called ML precision because it measures how many of the items the model labelled positive are actually positive, by using the formula given below:
Precision = TP / (TP + FP).
You want higher precision when false positives are costly. For example, if you flag bank transactions as fraudulent, each false alarm wastes investigator time. So, precision matters. Precision is one-half of the precision trade-off. The other half measures how many real positives you catch.
F1 Score in Machine Learning:
Sometimes you need a single number that balances precision and recall. That’s where the F1 score in machine learning comes in. If we take the harmonic mean of precision and recall, we get F1 as a result. The formula can be given as follows:
F1 = 2 * (precision * recall) / (precision + recall).
F1 punishes extreme imbalance between precision and recall more than the arithmetic mean. It rewards models that do well on both, not just one. Use F1 when you want a balanced view, and your classes are imbalanced, or when both false positives and false negatives hurt.
Accuracy Vs Precision Vs F1: Which Tool for Which Job?
Before going to a job, knowing the tool kit of a mechanic is very important:
- You can use accuracy for quick sanity checks when classes are balanced and errors cost equally.
- You can use precision (ML precision) when false positives are expensive.
- You can use recall when a positive is costly to miss (e.g., cancer screening).
- You can use the F1 score when you want a balanced single metric and both error types matter.
A good evaluation routine usually reports several of these metrics together so you see the full story, not a flattering snapshot.
Spam Filter Vs Medical Test: (A Real Example Explained.)
Imagine a spam filter. Regular email is just the same as a diagnostic test; if it is marked as spam, then it frustrates the users as a false positive. In contrast with the test, it also indicates we miss the disease in the report; it may signal a life-threatening factor. There, you prioritize recall. If stakeholders say, “Just give me accuracy,” ask them whether a single overall percentage really captures the cost of mistakes. Often it does not. Practical model evaluation matches the metric to the business risk.
Tricks to Test Your Accuracy Are Accurate or Not :
Before celebrating a high machine learning accuracy, check:
- Baseline models: What does a simple heuristic (always predict the majority class or random) get? If your model beats that alone, you have not done much.
- Cross-validation technique: It is a very important technique used to find accuracy when we divide the data into two parts. We often call it a lucky test set of data. If the test collapses eventually, you need to fix the issue soon.
- Confusion matrix: You can calculate the counts for TP/FP/FN/TN. Accuracy alone would not tell all types of errors.
Solid Methods to Check The Accuracy of A Machine Learning Model:
To check the accuracy of your ML model, you always need a short step-by-step guide that not only measures the accuracy but also assures you of the results:
- Try to split your data into train/ validation /test sets or use cross-validation for analysis purposes.
- You can use a reliable implementation, such as accuracy_score in scikit-learn, to calculate accuracy on unseen test data to get seen results.
- Analyze the confusion matrix to see error distribution.
- To calculate complement accuracy, compute precision, recall, F1, and possibly AUC to complement accuracy.
- You can compare your results with a simple baseline and check for data leakage.
- Based on your analysis, the classes are imbalanced; compute balanced accuracy or per-class metrics.
This routine gives you both the number and the story behind it.
FAQs:
Is 80% accuracy enough in machine learning?
Short answer: sometimes. If your baseline is much lower and the domain tolerates some mistakes (e.g., recommendations), 80% can be helpful. In high-risk domains (medicine, safety), you usually need much higher and a different mix of metrics.
Is 0.7 accuracy good?
A 0.7 (70%) accuracy may be perfectly acceptable for noisy, complex problems or early prototypes. But it could be weak for simpler tasks. The right move is to compare against baseline models, the business goal, and complementary metrics like F1. Do not accept 0.7 just because it looks clean. Check if it really solves the realistic problem or not.
What are the ways to check the accuracy of the Machine Learning model?
It can be calculated by an unseen test set or cross-validation. Analyze the confusion matrix, and report precision, recall, and F1 scores alongside accuracy. For imbalanced data, use balanced accuracy or class-wise metrics. In the end, compare your results with simple baselines and evaluate performance under realistic data shifts.
Conclusion:
Accuracy is a helpful compass. It provides a direction, offering a quick read on whether your model is roughly correct. But it is not the whole map. Use precision in machine learning, F1 score in machine learning, and other metrics to understand the nature of your model’s errors, and always tie metrics back to real consequences. If you treat accuracy as the final word, you will likely trip over hidden costs. Instead, let accuracy be one voice in a cacophony of metrics that together enable you to make a thoughtful and risk-calculating decision.
Reference Links:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2665917422000666
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/0144598718822400