Have you ever thought about how machines make intelligent choices even when things are difficult to understand? For example, how does your washing machine know that your clothes are “a little dirty” or “very dirty”?
Yes, this can be done by fuzzy logic. It’s an early idea that helped shape artificial intelligence (AI). Now, the machine is not giving answers like only “yes” or “no,” fuzzy logic lets computers think in between, like “maybe” or “somewhat.”
In this article, we will learn about fuzzy logic foundations in artificial intelligence, how fuzzy sets and early AI systems worked, and the role of fuzzy logic in intelligent computing with simple examples.
What Is Fuzzy Logic?
Fuzzy logic is an approach that deals with things that are not just “yes” or “no.” It was introduced by Lotfi A. Zadeh in 1965. For example, if it’s cold outside, with fuzzy logic, you might say it’s “sort of cold” or “very cold” instead of just “cold” or “not cold.” That means fuzzy logic uses a term (like 0 to 1) instead of only yes or no, or true or false.
Fuzzy Sets and Early AI Systems
One of the key building blocks of fuzzy logic is fuzzy sets. A fuzzy set lets something belong to a category partially instead of completely.
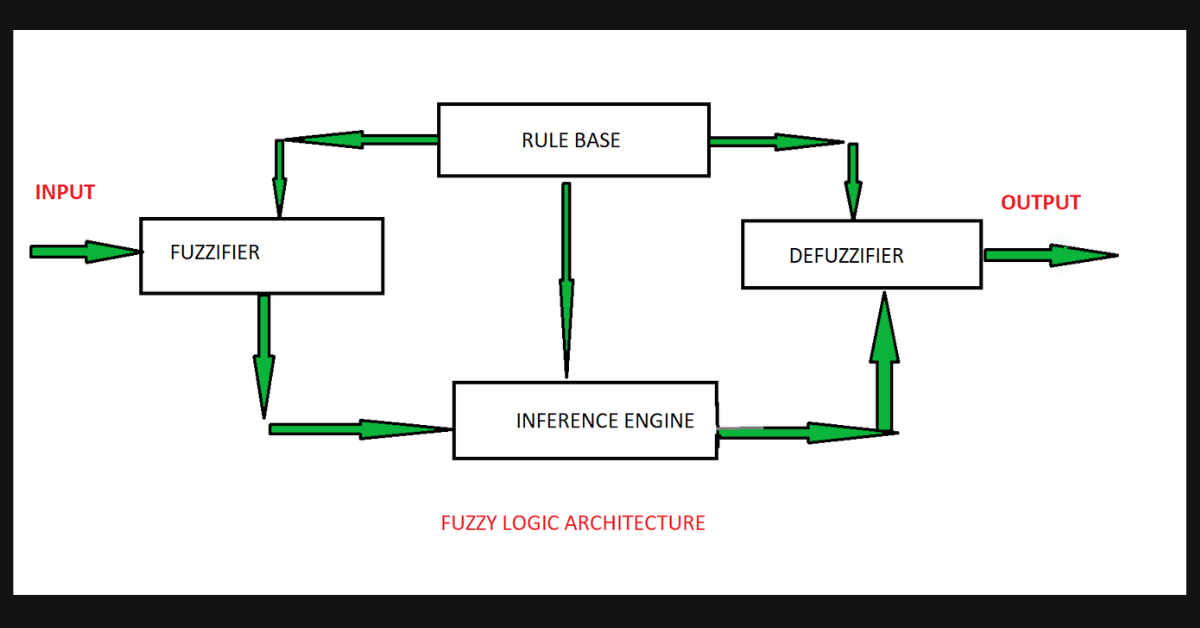
For example, a person might be “somewhat tall” rather than just tall or not tall. In early AI systems, fuzzy logic helped machines make decisions when things were unclear. For example, Japanese washing machines use fuzzy logic to decide how much water or soap to use based on how dirty the clothes are
Fuzzy Logic Foundations in Artificial Intelligence
Now, let’s explore the role of fuzzy logic in the development of modern AI. Fuzzy logic provided the ability for computers to deal with uncertain or “fuzzy” data (like “warm”, “cool”, “fast”, “slow”), which made it a key factor in intelligent computing. It enables the systems to imitate human-like reasoning rather than being limited to hard and fast rules.
In various AI systems, fuzzy logic collaborated with other techniques (e.g., neural networks). This approach made it possible for machines to tackle real-world problems where the solution is not purely yes or no. This is why we can say that fuzzy logic was among the very first stepping stones and one of the pillars of artificial intelligence.
Role of Fuzzy Logic in Intelligent Computing
When we talk about intelligent computing, we mean computers or robots that can solve problems just like humans. Fuzzy logic’s role in intelligent computing is to enable these machines to handle “gray areas” other than only making black-and-white decisions.
Here is a real-life example:
Self-driving cars: This is fuzzy logic work that makes quick decisions according to the situation, like “If a person is close to the car in front and the speed is high, fuzzy logic should brake a little faster.”
Was Fuzzy Logic a Precursor to AI?
Yes, we can say that fuzzy logic helped start the path toward AI. Let’s take a look at how:
- Fuzzy logic introduced the idea that machines could deal with uncertainty and indistinct concepts, just like humans.
- It helped to create many “smart” machines and systems before the advanced AI we use today.
Simple Example to Understand
Suppose you’re in class and your teacher asks, “Are you tired?” With regular logic, you say “Yes” or “No.”
But with fuzzy logic, you can say “I’m 0.6 tired” (a little tired) or “0.9 tired” (very tired).
If the teacher’s computer system used fuzzy logic, it might say: “As you’re 0.6 tired, you can take a short break.”
This example shows how fuzzy logic enables machines to think more naturally, like human beings.
FAQs
1. Is fuzzy logic related to AI?
Yes, fuzzy logic is related to AI. It is one of the early ideas that helped to shape artificial intelligence. It teaches machines how to make decisions when things are not completely true or false. For example, fuzzy logic helped an AI-powered air conditioner to decide whether a room is “a little warm” or “very warm” — not just “hot” or “cold.”
2. Is AI just fuzzy logic?
No, AI is not just fuzzy logic. Fuzzy logic is just a small part of artificial intelligence. There are many other fields included in AI, like machine learning, neural networks, and natural language processing.
3. What type of logic is used in AI?
AI uses different types of logic depending on the problem. Some common types are:
- Boolean logic: for clear yes/no (true/false) decisions.
- Fuzzy logic: for decisions that are not exact (for example, “somewhat fast” or “a little slow”).
- Probabilistic logic: for making choices when the outcome is unsure.
Among these, fuzzy logic is special because it helps AI systems act more like humans — making flexible, realistic decisions instead of rigid ones.
4. What is a fuzzy model in AI?
A fuzzy model in AI is a system that uses fuzzy rules to make intelligent choices. It doesn’t need exact numbers; rather, it can work with words like “low,” “medium,” and “high.”
For example, “If traffic is heavy in harsh weather conditions, then increase the green light time.”
This shows that the fuzzy model looks at the situation and decides the best action, similar to how humans would.
Conclusion
Simply, fuzzy logic helped computers think more like humans by allowing “kind of true” or “sort of true” instead of only “true” or “false.” That made it a major milestone in the development of AI. By understanding fuzzy logic, we see how computers started to handle real-world, unclear situations and which opened the door for modern AI systems. Moreover, fuzzy logic truly was one of the early precursors to AI, especially in how machines learned to deal with everyday uncertainty.
REFERENCES:
https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-1-4020-9119-3_6