AI is ruling the world right now. Every day, you get to know about some other AI models in the market, but these tools are not 100% accurate. They make mistakes and give unreliable results. You might have faced it too and must have blamed the model for it. The fault is not in the model that the answers are not satisfactory. The real problem lies deep within the data set that was given to the machine learning model. This is where the concept of Shannon entropy enters the chat.
What Is Entropy in Machine Learning
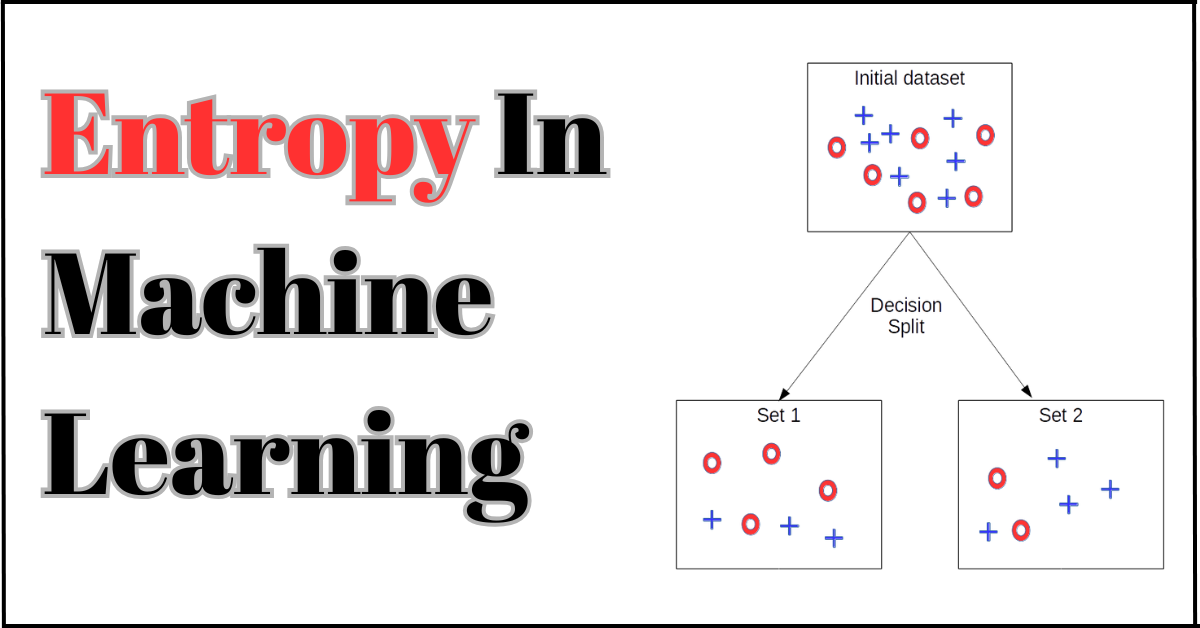
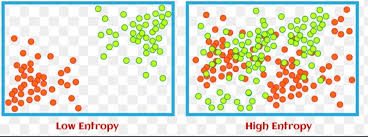
Entropy was first introduced in thermodynamics and later spread to other fields such as math, statistics, and machine learning. In textbook terms, it is a quantitative variable that measures the amount of uncertainty or randomness in the dataset. In simple words, it is the cluttered data provided to a machine learning algorithm. If the entropy is low, it is favorable for you, as your ML will learn quickly and predict accurately. But if the entropy is high, your system will provide less reliable, and confusing data to users.
What is a Real example of entropy?
If still, after the above explanation, the question What is the concept of entropy? puzzles your mind, Let’s understand it with a simple analogy. For example, there are 100 students in one class. If 50 pass and 50 fail, the entropy is high, because the system won’t be able to predict the possible outcome. If 70 pass and 30 fail, the entropy is low, as the system will easily predict the possible outcome of the situation.
What is Entropy in Decision Trees?
Entropy is the backbone of the decision tree algorithm. It helps the decision tree make the right data split. It makes the model more straightforward, transparent, and easier to understand, thereby increasing the AI model’s reliability.
Now, the question that might be puzzling your brain is What is a Decision Tree?.A Decision tree mirrors how a flowchart works. A flowchart organizes information to create a clear picture of context, in the same way a decision tree divides data to minimize noise. The decision tree examines different features, then calculates each feature’s entropy.
If a feature has less entropy, the decision tree splits the data accordingly. For instance, the system has two features to evaluate whether students pass the class. One shows attendance, and the other shows the number of hours the student studies. The hours feature reports lower entropy, so the decision tree will split the data based on the hours feature.
How The System Calculates Entropy
After theoretically understanding entropy and its importance, let’s get to the complicated part: how does the machine perform calculations?
H(X) = -∑ p(x) * log₂(p(x)
Decision tree uses this equation to do all the calculations before splitting the data, where:
H= entropy
p=probability
Log2 = surprise value
Surprise value is inversely proportional to probability: the less expected the outcome, the greater the surprise. The decision tree collects data on the likelihood of different features and applies them in the formula to get entropy.
Is Entropy Always The Bad Guy
The clear answer is no, that’s not the case at all. The key in machine learning is the right balance between the data set and high entropy. Also, it has some good points! Yes, that’s right: the high entropy values suggest there is a vast amount of data to choose from. Unless we are going for deep details or compilation, it is not of use to us. Low entropy, seems excellent but yields less data and is more straightforward, making predictions easier for the machine.
FAQ’s
Q1: What Is The Concept Of Entropy?
Entropy is a borrowed concept from thermodynamics. It describes the disorganized, messy data that machine learning systems struggle to interpret. That leads to unreliable and less confident responses. High entropy indicates less confident responses, while low entropy indicates more confident responses.
Q2: What Is Entropy In Decision Trees?
Entropy plays a key role in decision trees; the decision tree works like a flowchart. It splits the data using the most appropriate features, based on entropy. The decision tree calculates entropy to divide the data accordingly.
Q3: What Is Entropy In NLP?
For NLP (Natural Language Processing), entropy shows how confidently the system predicts the exact Word. If the system predicts correctly, the language model is considered good because it has low entropy. Similarly, if the model fails to indicate the correct Word, the model is not preferred for translation or language-related tasks.
Conclusion:
Entropy is an integral part of machine learning. It is a quantitative measure that symbolizes the randomness and disorganization of the data. Decision-tree-based models rely on entropy to make data easily accessible for learning. AI models use this data to generate responses quickly and most importantly, accurately. If entropy is low, the model is good; if it is high, it might lack the concept of precision.
References:
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/machine_learning/machine_learning_entropy.htm